What are Reciprocating Compressors?

Reciprocating compressors, also known as piston compressors, are positive displacement compressors that use pistons driven by a crankshaft to deliver gases at high pressure.
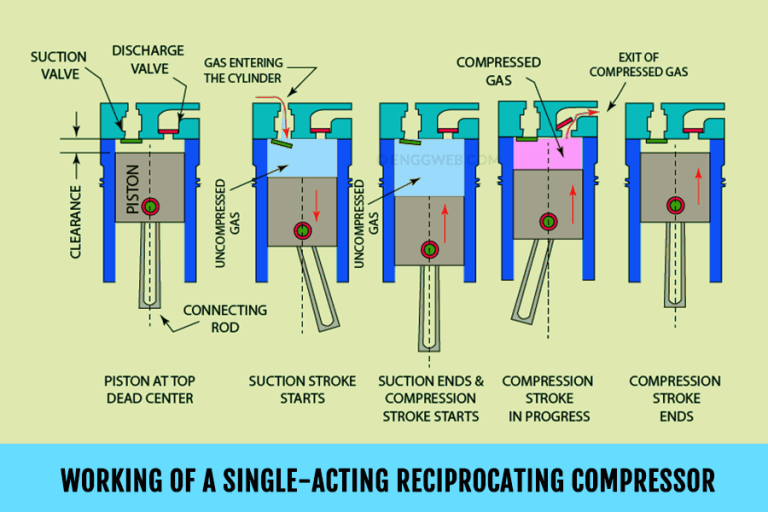
These compressors work on the principle of increasing the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume through a reciprocating (back and forth) motion. The intake gas is drawn into a compression cylinder, where a piston compresses it and then discharged at a higher pressure.
This process is repeated continuously, making these compressors highly effective for various industrial applications.
The Working Principle Explained
Reciprocating compressors, or piston compressors, operate based on the principle of a positive displacement, which involves trapping a specific volume of gas and then compressing it to a higher pressure. The core of this mechanism is the piston, which moves in a reciprocating motion inside a cylinder.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how this works:
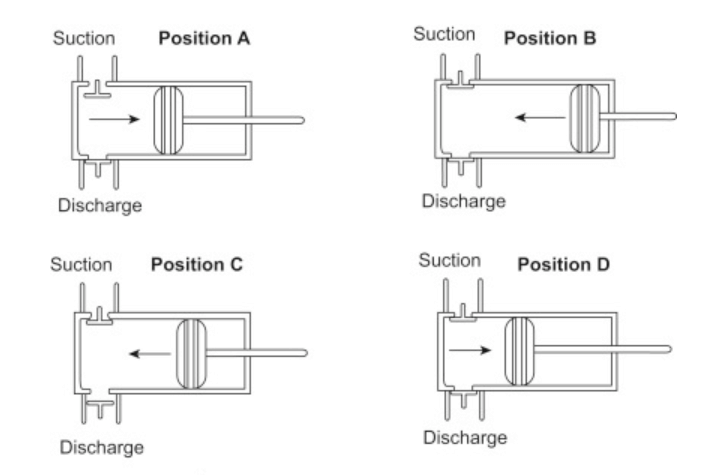
1. Intake Phase (Position A): During the intake stroke, the piston moves backwards, reducing the pressure inside the cylinder. This causes the suction valve to open, allowing the gas to enter the cylinder.
2. Compression Phase (Position B): As the piston moves upward, it compresses the gas, increasing its pressure. The suction valve closes, ensuring that no gas escapes.
3. Discharge Phase (Position C): When the gas reaches the desired pressure, the discharge valve opens, allowing the compressed gas to exit the cylinder and be delivered to the desired destination.
4. Cycle Repeat: This cycle repeats continuously, enabling the compressor to provide a steady flow of compressed gas.
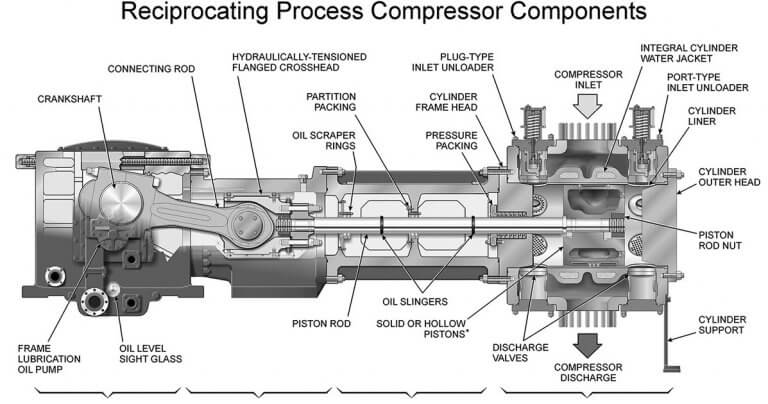
Key Components of the Reciprocating Compressor
Pistons: The piston is the primary moving component that compresses the gas. It is driven by the crankshaft and moves in a linear motion within the cylinder.
Crankshaft: The crankshaft converts the motor’s rotary motion into the piston’s linear reciprocating motion. It plays a crucial role in the overall functioning of the compressor.
Cylinders: The cylinder is the chamber where the gas is compressed. It houses the piston and contains the intake and discharge valves.
Valves: The intake and discharge valves control the gas flow into and out of the cylinder. These valves open and close automatically based on the pressure differential, ensuring efficient gas flow and compression.
Types of Reciprocating Compressors
Reciprocating compressors come in various configurations, each suited to specific applications and operational needs. Understanding the differences between these types can help in selecting the right compressor for your requirements. Here are the primary types of reciprocating compressors:
Single-Acting vs. Double-Acting Compressors
Single-Acting Compressors: In a single-acting reciprocating compressor, the gas compression occurs on only one side of the piston during its stroke. This type is simpler in design and is typically used for lower-capacity applications. The single-acting design is effective for situations where lower pressure and flow rates are sufficient.
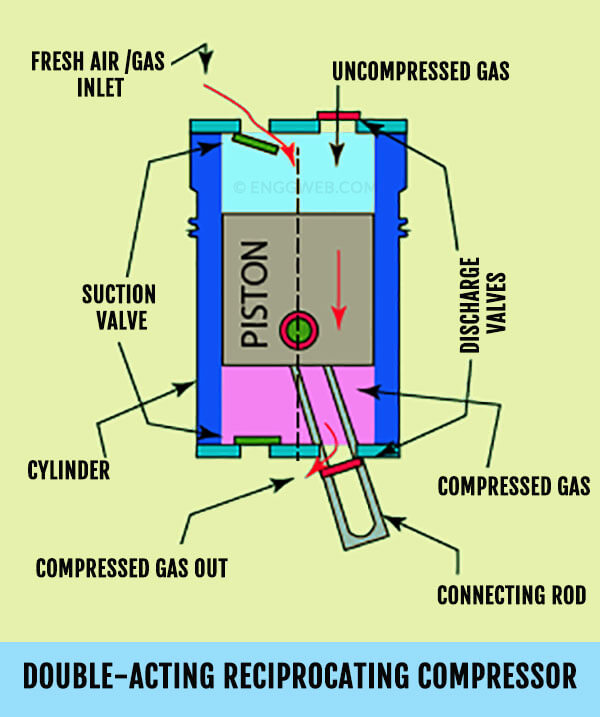
Double-Acting Compressors: Double-acting compressors compress gas on both sides of the piston during each stroke, making them more efficient and capable of higher capacity compared to single-acting compressors. This design allows for a more continuous and balanced flow of compressed gas, making it suitable for industrial applications that require higher pressures and flow rates.
Air-Cooled vs. water-Cooled Compressors
Air-Cooled Compressors: In air-cooled compressors, the heat generated during the compression process is dissipated using ambient air. This cooling method is straightforward and requires less maintenance compared to water-cooled systems. Air-cooled compressors are ideal for small to medium-sized applications where the ambient temperature can efficiently cool the compressor.
Water-Cooled Compressors: Water-cooled compressors use water as a cooling medium to remove the heat generated during compression. This type of cooling is more efficient and effective for high-capacity compressors that operate continuously or under heavy loads. Water-cooled compressors are commonly used in industrial settings where maintaining a stable operating temperature is crucial for performance and longevity.
Oil-Lubricated vs. Oil-Free Compressors
Oil-Lubricated Compressors: These compressors use oil to lubricate the moving parts, reducing friction and wear. The oil also helps in sealing the compression chamber, enhancing the efficiency of the compression process. Oil-lubricated compressors are durable and suitable for a wide range of industrial applications. However, they require regular maintenance to manage the oil levels and prevent contamination of the compressed gas.
Oil-Free Compressors: Oil-free compressors do not use oil for lubrication within the compression chamber. Instead, they rely on alternative methods such as Teflon coatings or other advanced materials to reduce friction. These compressors are essential in applications where the presence of oil could contaminate the end product, such as in the food, pharmaceutical, and electronics industries. Although they require less maintenance related to oil management, oil-free compressors may have higher initial costs and may wear out faster than oil-lubricated ones.
Each type of reciprocating compressor offers unique benefits and is suited to specific operational needs. By understanding these differences, you can select the compressor that best fits your application, ensuring efficiency, reliability, and longevity.
Real-World Applications of Reciprocating Compressors
Reciprocating compressors are incredibly versatile and are utilized in a wide array of industrial and everyday applications. Their ability to generate high pressures and handle various gases makes them indispensable in many sectors.
Below are some key real-world applications:
Industrial uses: Oil refineris, gas pipeline, chemical plants
Oil Refineries:
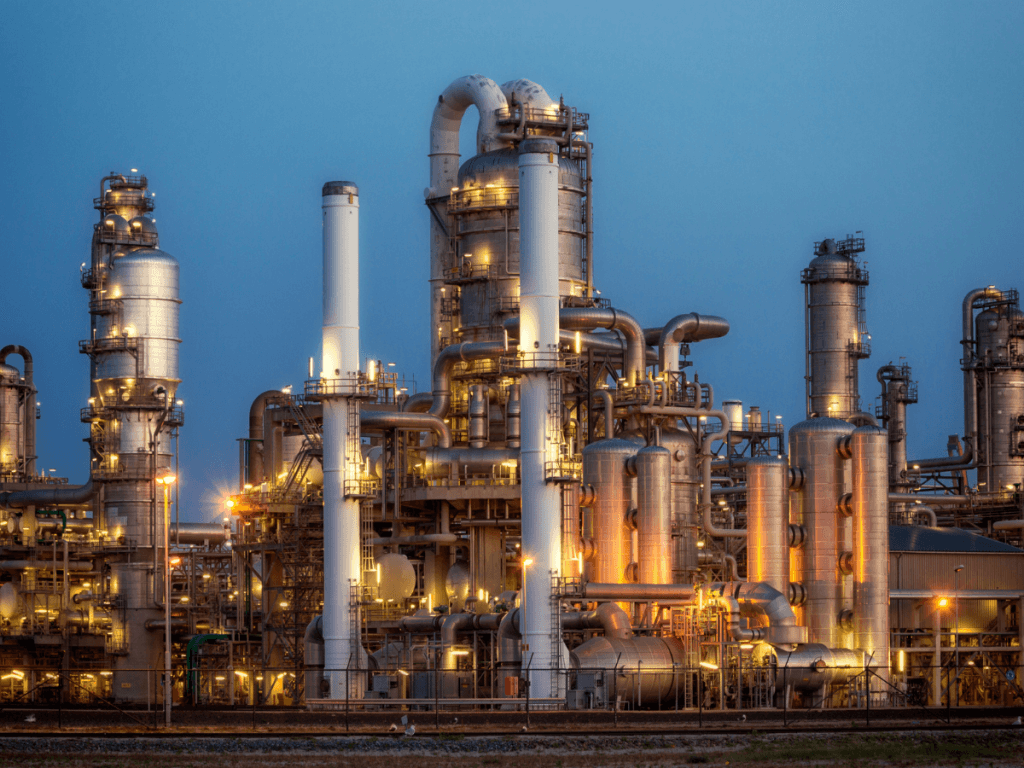

In oil refineries, reciprocating compressors are used to compress hydrocarbon gases, enabling efficient transportation and processing. These compressors are vital in processes such as catalytic cracking and hydrocracking, where maintaining high pressures is essential for converting crude oil into valuable products like gasoline and diesel.
Gas Pipelines:

Reciprocating compressors are essential for maintaining the pressure in gas pipelines. They help boost natural gas pressure to ensure smooth and efficient transportation over long distances. This application is critical in ensuring the continuous supply of natural gas to residential and industrial users.
Chemical Plants:

In chemical manufacturing, reciprocating compressors are used to compress and transport various gases required in chemical reactions. These compressors ensure that the gases are delivered at the required pressures and volumes, facilitating efficient and safe chemical production processes. They are also used in the synthesis of chemicals, where precise pressure control is crucial.
Everyday Applications: Air conditioning, refrigeration
Air Conditioning: Reciprocating compressors play a significant role in air conditioning systems by compressing the refrigerant gas. The compressed gas is then cooled and expanded to provide the cooling effect needed for air conditioning. These compressors are commonly found in residential, commercial, and industrial air conditioning units, ensuring comfortable indoor environments.
Refrigeration: Similar to air conditioning, reciprocating compressors are used in refrigeration systems to compress refrigerant gases. This process is essential for preserving food and other perishable items by maintaining low temperatures. Refrigeration systems equipped with reciprocating compressors are used in a variety of settings, including household refrigerators, commercial freezers, and large-scale industrial refrigeration units.
Why Choose Reciprocating Compressors?
Reciprocating compressors offer several advantages that make them suitable for a wide range of applications:
Refrigerated Dryers

Suitability: Common choice for industrial applications. Cools air to remove moisture, then reheats to an optimal temperature.
Applications: Suitable for general manufacturing, automotive shops, and scenarios requiring dry air without extreme conditions.
Dew Point: Ranging from approximately 3°C to 10°C, suitable for standard industrial environments.
Desiccant Dryers

Suitability: Ideal for high-demand situations requiring extremely dry air.
Utilizes absorbent materials for moisture extraction, achieving a significantly lower dew point.
Applications: Perfect for critical environments like laboratories, food processing, electronics manufacturing, and paint spraying.
Dew Point: Reaching extremely low dew points, such as -40°C or even -70°C, suitable for the most stringent applications.
High Pressure Capabilities
Reciprocating compressors can achieve very high pressures, making them ideal for applications that require intense gas compression. This capability is essential in industries such as oil and gas, where high-pressure gas transport and processing are critical.
Efficiency
These compressors are highly efficient in terms of energy consumption and performance. They can compress gas to high pressures with relatively low energy input, which translates to cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
Versatility Across Various Applications
The versatility of reciprocating compressors is another significant advantage. They can handle different types of gases and pressures, making them suitable for diverse applications ranging from industrial processes to everyday systems like air conditioning and refrigeration. Their adaptability to various operational requirements ensures that they can meet the specific needs of different industries.
Comparing Reciprocating Compressors to Other Types
Refrigerated Dryers

Suitability: Common choice for industrial applications. Cools air to remove moisture, then reheats to an optimal temperature.
Applications: Suitable for general manufacturing, automotive shops, and scenarios requiring dry air without extreme conditions.
Dew Point: Ranging from approximately 3°C to 10°C, suitable for standard industrial environments.
Desiccant Dryers

Suitability: Ideal for high-demand situations requiring extremely dry air.
Utilizes absorbent materials for moisture extraction, achieving a significantly lower dew point.
Applications: Perfect for critical environments like laboratories, food processing, electronics manufacturing, and paint spraying.
Dew Point: Reaching extremely low dew points, such as -40°C or even -70°C, suitable for the most stringent applications.
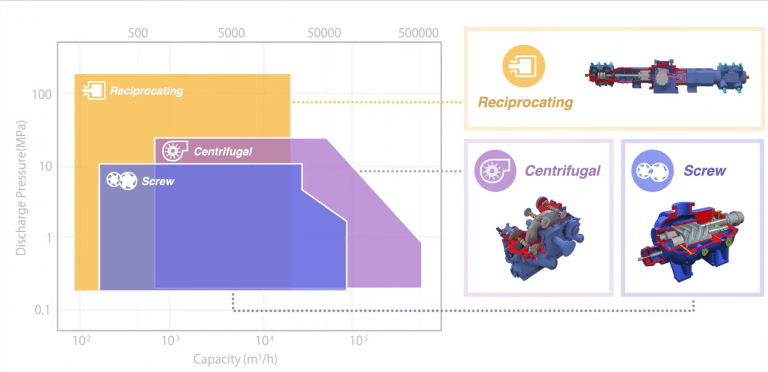
Reciprocating vs. Rotary Compressors
Reciprocating Compressors: These compressors use a piston and cylinder mechanism to compress the gas. They are known for their ability to achieve high pressures and are suitable for applications requiring precise pressure control. However, they can be noisier and may require more maintenance compared to rotary compressors.
Rotary Compressors: Rotary compressors use rotating elements such as screws or vanes to compress gas. They are generally quieter, more compact, and require less maintenance. Rotary compressors are often used in applications where noise levels and space constraints are critical factors. However, they may not achieve the same high pressures as reciprocating compressors.

Reciprocating vs. Centrifugal Compressors
Reciprocating Compressors: As mentioned, these compressors are ideal for high-pressure applications and provide efficient gas compression for various industrial processes. They are suitable for lower flow rates and higher pressures.
Centrifugal Compressors: Centrifugal compressors use a rotating impeller to impart velocity to the gas, converting it into pressure. They are well-suited for applications requiring high flow rates and are often used in large-scale industrial processes. Centrifugal compressors are typically more efficient for continuous, large-volume gas compression but may not achieve the same high pressures as reciprocating compressors.

By understanding the specific benefits and applications of reciprocating compressors, industries can make informed decisions about the best type of compressor to use.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Reciprocating Compressor
Pressure Requirements
When selecting a reciprocating compressor, understanding the pressure requirements of your application is crucial. Different processes demand varying levels of pressure, and the compressor must be capable of meeting these demands.
High-Pressure Applications: Gas pipelines, chemical plants.
Low-Pressure Applications: Air conditioning systems.
Air Quality Needs
Additionally, the quality of air needed is another important factor.
Some applications, like those in the food and pharmaceutical industries, require oil-free air to avoid contamination. In such cases, oil-free reciprocating compressors are the best choice.
Conversely, general industrial applications might be well-suited to oil-lubricated compressors, which offer durability and efficiency.
Operational Hours and Usage Patterns
The operational hours and usage patterns of the compressor should also influence your choice. Compressors that run continuously or under heavy loads need to be robust and reliable.
Continuous Use: Heavy-duty, water-cooled compressors for round-the-clock operations (manufacturing plants).
Intermittent Use: Air-cooled compressors for applications with sporadic use (small workshops)
Ensuring Proper Sizing and Selection
Maintenance Considerations for Long-Term Reliability
Proper maintenance is key to ensuring the long-term reliability of reciprocating compressors. Regular inspection and servicing can prevent breakdowns and extend the lifespan of the equipment. Oil-lubricated compressors, for example, require regular oil changes and monitoring to avoid contamination and ensure smooth operation.
Components like piston rings, valves, and filters must also be checked and replaced to maintain efficiency and performance.
Tips for Optimal Performance and Longevity
Regular Maintenance: Establish a routine maintenance schedule that includes checking for wear and tear, oil levels, and component integrity. Regular maintenance not only prevents unexpected failures but also enhances the overall performance of the compressor.
Proper Sizing: Ensure the compressor is appropriately sized for your application. An undersized compressor may overheat and fail prematurely, while an oversized one can be inefficient and costly. Understanding your operational needs and selecting a compressor that matches those requirements is crucial.
Quality Installation: Proper installation is essential for optimal compressor performance. This includes ensuring adequate ventilation, appropriate mounting, and alignment of components. Poor installation can lead to operational issues and reduced efficiency.
Monitoring and Control: Implement monitoring systems to keep track of the compressor’s performance. Modern compressors often come with digital controls and sensors that provide real-time data on pressure, temperature, and operational status. Utilizing these tools can help in early detection of potential problems and allow for timely intervention.
Training and Safety: Ensure that operators are well-trained in the use and maintenance of the compressors. This includes understanding safety protocols and operating procedures to prevent accidents and ensure the compressor is used correctly.
By considering these factors and following best practices, you can select a reciprocating compressor that meets your operational needs and ensures long-term efficiency and reliability.
Comprehensive Solutions by Air to Air Engineering
At Air to Air Engineering, we offer a wide range of high-quality air compressors tailored to meet the diverse needs of various industries. Our products are designed with precision engineering and advanced technology to ensure optimal performance, efficiency, and reliability.
Get in touch with us
At Air to Air Engineering, we are committed to providing exceptional customer service and support. Whether you need help selecting the right compressor or require maintenance services, our team is here to assist you. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you choose the right air compressor for your application!
ELGi Air Compressors
We are trusted ELGi Screw Air Compressor specialist in Johor Bahru, offering High-Performance ELGi Air compressors. Contact us today for superior performance!
KOBELCO Air Compressors
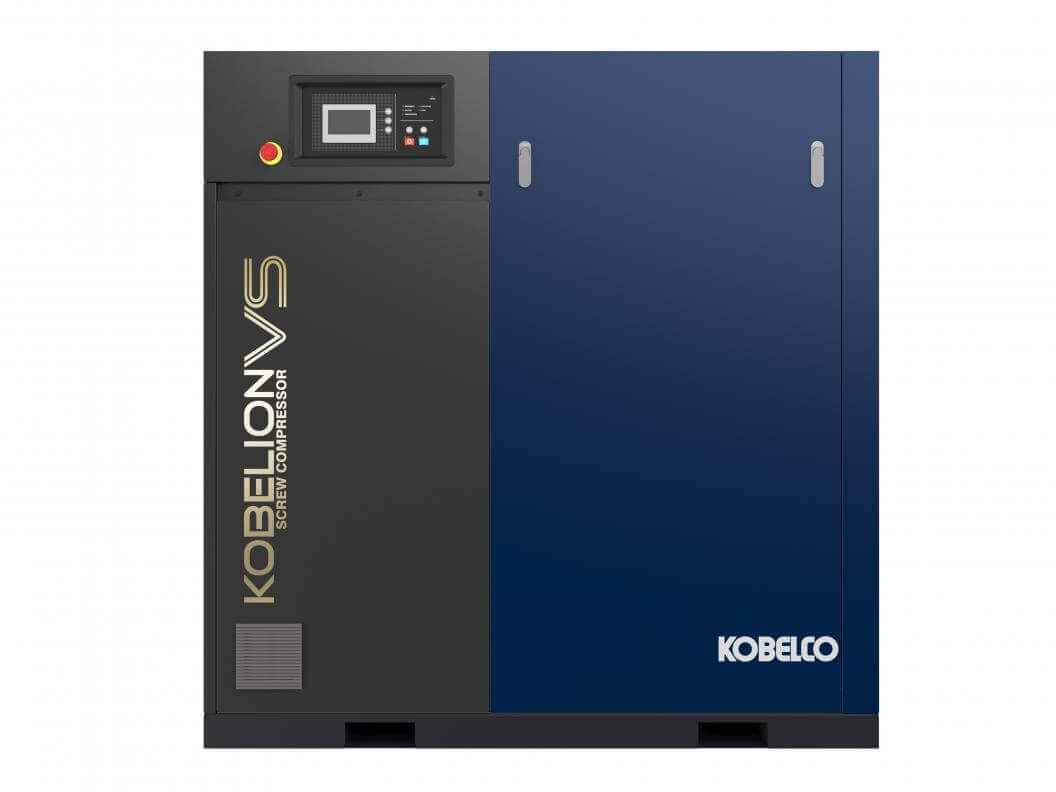

Discover reliable wide range of KOBELCO compressors from us. Contact us today to get top-quality products and exceptional service!