Air compressors are essential machines that play a crucial role in various industries, from construction and manufacturing to automotive and beyond. Whether you’re inflating tyres, powering tools, or managing large-scale operations, understanding how air compressors work can help you make more informed decisions for your operation.
For expert advice on selecting or maintaining an air compressor, Air to Air Engineering offers top-tier services, including industrial air compressor sales, maintenance, and rental services for leading brands like ELGi and KOBELCO.
In this guide, we’ll break down the main components of an air compressor in simple, easy-to-understand terms. We’ll explore the two primary types—reciprocating and rotary screw compressors—each suited for different tasks and levels of usage.
The key parts of an air compressor include the motor, which drives the machine, and the compressor pump, which compresses the air. The air is then stored in a tank, ready for use. Alongside these are vital supporting parts like pressure gauges that monitor tank pressure and safety valves that prevent over-pressurization, ensuring safe operation.
Regular maintenance is also essential for keeping your air compressor in top working condition. Simple tasks like changing the oil and replacing filters can significantly extend the life of your machine.
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a solid understanding of your air compressor’s components and how to maintain it, helping you get the most out of your investment.
What is Compressed Air?
Compressed air is regular air that has been squeezed into a smaller space, which increases its pressure and stores energy. This process happens inside an air compressor, where power is converted into compressed air.
This high-pressure air is incredibly useful for a wide range of tasks, from inflating tyres and powering tools to running heavy machinery. Different types of air compressors, such as reciprocating, rotary screw, rotary vane, and centrifugal, are designed to handle various jobs depending on the needs of your business.


Compressed air is considered a vital resource, often referred to as the “fourth utility” alongside water, electricity, and gas. It’s a flexible and versatile energy source, commonly used in situations where electricity might pose a safety risk. For instance, compressed air is preferred in environments where sparks or overloads from electrical equipment could be dangerous.
When working with compressed air, two key measurements are important: PSI (pounds per square inch) and CFM (cubic feet per minute). PSI tells you the air pressure, while CFM indicates the airflow rate. Both are crucial for ensuring your compressor meets the demands of your specific tasks.
Regular maintenance is essential to keeping your air compressor in top shape. This includes changing the oil, replacing filters, and performing safety checks to ensure everything runs smoothly and safely.
To ensure you’re using the most efficient system, consult with Air to Air Engineering. Our team can help you optimize your setup and reduce energy costs with our comprehensive maintenance services.
Components of an Industrial Compressed Air System
A compressed air system consists of several key components, including the air compressor, air receiver, air dryer, filters, and valves. Each plays a vital role in the system’s overall performance. Understanding these parts can help you make informed decisions when purchasing, using, and maintaining an air compressor.
Air Compressor and Motor
The air compressor is the central part of the system, responsible for compressing air and increasing its pressure. It’s essentially the engine that drives everything else, ensuring that you have a reliable source of compressed air for your tasks.
The compressor motor powers this process, with different types of motors (electric or gasoline) being used depending on the system’s size and requirements.
Air End (For Rotary Screw Compressors)
In rotary screw compressors, the air end compresses the air using interlocking rotors. This mechanism is highly efficient and is often used in applications that require continuous operation.
Compressor Pump (For Reciprocating Air Compressors)
For reciprocating air compressors, the compressor pump uses a piston and cylinder setup to compress the air. This type of pump is ideal for smaller, portable compressors and can be either single-stage or two-stage, depending on the pressure needs.
Air Receivers (Storage Tank)
The air receiver, or storage tank, is where compressed air is stored until it’s needed. It helps regulate the air pressure and ensures that you have a steady supply of air, even when the compressor isn’t actively running. Smaller tanks are ideal for occasional use, while larger tanks are better suited for continuous operations.
Air Dryer
An air dryer is essential for removing moisture from the compressed air. Moisture can cause rust and damage to your tools and equipment, so drying the air is crucial for maintaining a clean and efficient system.
Compressed Air Filters
Filters are used to remove contaminants from the air, such as dust, dirt, and oil. These particles can clog the system and reduce efficiency, so keeping the air clean with regular filter maintenance is important.
Valves
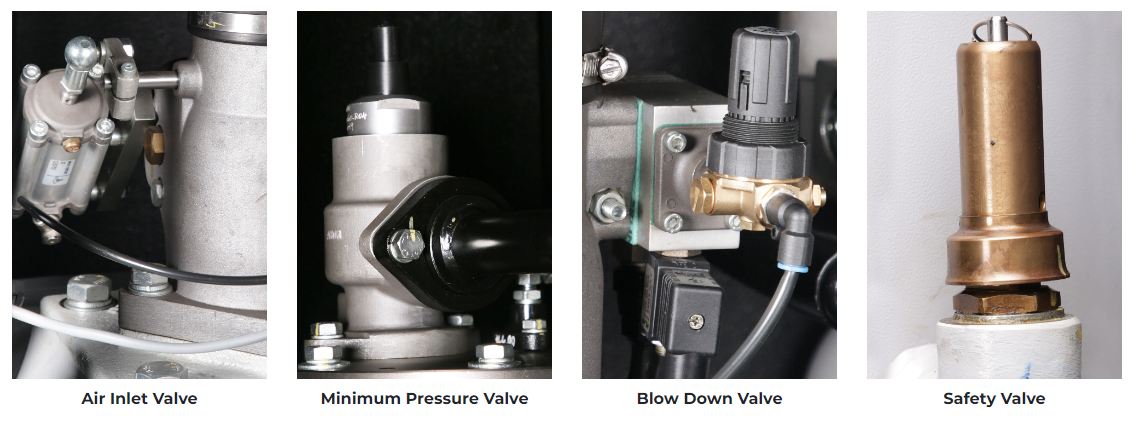
Valves play several roles in managing the air compressor’s operation. They help control airflow, manage pressure, and ensure safety by preventing over-pressurization.
The safety pressure relief valve prevents over-pressurization by releasing excess air when needed.
The unloader valve assists in the smooth start-up of reciprocating air compressors by releasing trapped air when the compressor is not running.
Pressure Gauges
Pressure gauges are used to monitor the air pressure within the system, ensuring it stays at the correct level for safe and efficient operation.
How Does a Compressed Air System Work?
Understanding how a compressed air system works can help you better appreciate the role of each component. Here’s a simple breakdown of the process:
Air Intake: The compressor draws in air from the surrounding environment. This air enters the system and is directed into the compression chamber.
Compression: Inside the compressor, the air is squeezed into a smaller space, increasing its pressure. Depending on the type of compressor, this might involve a piston and cylinder (in reciprocating compressors) or interlocking rotors (in rotary screw compressors).
Energy Generation: The compressor’s motor and pump work together to generate the energy needed for this process, transforming electrical or mechanical power into compressed air.
Storage: Once compressed, the high-pressure air is sent to the air receiver or storage tank. Here, it is stored until needed, ensuring a steady supply is available.
Distribution: When required, the compressed air is distributed to various devices and machinery through a network of pipes, valves, and regulators. The system ensures that air is delivered at the correct pressure for each application.
A well-functioning compressed air system is vital for any industrial operation. Air to Air Engineering provides expert maintenance and rental services, so you can keep your operations running without a hitch. Contact us today to learn how we can support your business.
Maintaining a Compressed Air System
Regular maintenance is crucial to keeping your compressed air system running smoothly and preventing costly problems down the line. Without proper care, issues like clogged filters can develop, causing a drop in air pressure and forcing the compressor to work harder, which can lead to increased energy costs and potential breakdowns.
Here are some essential maintenance tips to ensure your system performs as intended:
- Schedule Professional Servicing: It’s a good idea to have your compressed air system professionally serviced at least once a year. A professional can identify and fix any issues before they become major problems, ensuring your system stays in top condition.
- Keep Air Filters Clean: The air filter cleans the air before it enters the compressor, preventing dust and dirt from causing damage. Regularly checking and replacing the air filters can improve your system’s efficiency, potentially reducing electricity usage by 5–15%.
- Check and Maintain Drain Valves: Drain valves are essential for removing the accumulated water in the storage tank. If this water isn’t drained regularly, it can cause rust and other damage. Manual or automatic drain valves should be checked often to ensure they function properly.
- Replace Worn Parts: Over time, parts like filters, hoses, and valves will wear out and need replacing. Monitoring these components and replacing them as needed can prevent unexpected breakdowns and keep your system running efficiently.
- Use the Right Accessories: Accessories like pressure regulators, couplers, and hose attachments can help your compressor work more efficiently and safely. For example, pressure regulators control the amount of pressure in the system, ensuring that your tools and machinery receive the right amount of air.
By following these maintenance tips and regularly checking your air compressor, you can extend its lifespan, reduce energy costs, and ensure it performs reliably for all your business needs.
Need Help?
If you need professional assistance in maintaining or upgrading your system, Air to Air Engineering is here to help. We specialize in servicing ELGi and KOBELCO compressors, ensuring your system runs smoothly and efficiently.
Common Mistakes To Avoid With Compressed Air
Using compressed air effectively is key to keeping costs down and ensuring your system operates efficiently.

However, there are some common mistakes that many businesses make, which can lead to unnecessary expenses and reduced performance.
Here’s how to avoid them:
Treating Compressed Air as a Free Resource One of the most common mistakes is treating compressed air as an unlimited, free resource. Operators might use compressed air in industrial settings for tasks like cleaning dirt or water off parts. However, compressed air is far from free—it’s actually one of your facility’s most expensive forms of energy. Misuse can lead to higher energy bills and wear on your system. Instead, consider using alternative methods for cleaning or invest in more efficient air nozzles designed to minimize air consumption.
Ignoring Air Leaks Air leaks are a major source of energy waste in compressed air systems, often wasting as much as 20%-30% of the compressor’s output. Regularly inspect your system for leaks, particularly around joints, connections, and hoses. Using leak detection tools or even a simple soapy water solution can help you identify and fix these leaks before they become costly.

3. Over-Pressurizing the System It’s a common misconception that running your compressor at a higher pressure will improve performance. In reality, over-pressurizing your system can increase energy consumption by up to 10% for every 2 PSI of unnecessary pressure. It can also cause excess wear and tear on your equipment. To avoid this, ensure your system is set to the appropriate pressure for your specific applications, and use pressure regulators to maintain the correct levels throughout your operations.
4. Neglecting Regular Maintenance Skipping regular maintenance is a mistake that can lead to costly downtime and repairs. As mentioned earlier, maintaining clean air filters, checking drain valves, and replacing worn parts are essential for keeping your system in good shape. A well-maintained compressor operates more efficiently and has a longer lifespan, saving you money in the long run.

5. Failing to Match Compressor Size to Demand Another common mistake is using a compressor that is either too large or too small for your needs. An oversized compressor will waste energy by producing more air than necessary, while an undersized compressor will struggle to meet demand, leading to increased wear and reduced lifespan.
By avoiding these common mistakes and following best practices, you can significantly improve the efficiency of your compressed air system, reduce energy costs, and extend the life of your equipment.
If you’re concerned about inefficiencies or need help optimizing your system, Air to Air Engineering is your go-to partner for expert advice and service. Let us help you avoid costly errors and maximize your system’s performance.
Creating an Efficient Compressed Air Environment

Setting up your compressed air system in the right environment is crucial for maximizing its efficiency, performance, and lifespan. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind:
Ensure Proper Ventilation Placing your air compressor in a well-ventilated area is essential. Adequate airflow helps dissipate the heat generated during compression, preventing the system from overheating. Overheating can reduce the efficiency of your compressor and may lead to premature wear and potential breakdowns. Industry experts, such as those at the Compressed Air & Gas Institute (CAGI), recommend placing your compressor in a location where there is a steady flow of cool, clean air to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
Maintain Reasonable Temperatures The temperature of the environment where your air compressor operates can significantly impact its performance. Extreme temperatures—whether too hot or too cold—can affect the viscosity of the compressor oil and the overall efficiency of the system. Ideally, keep the ambient temperature within the manufacturer’s recommended range to ensure smooth operation. This not only improves efficiency but also extends the life of your compressor by reducing strain on its components.
Control Humidity Levels High humidity can introduce moisture into your compressed air system, leading to rust, corrosion, and damage to tools and equipment downstream. To combat this, ensure the area where your compressor is located has low humidity levels. Additionally, using air dryers and moisture separators can help remove excess moisture from the air before it enters the compressor, further protecting your system from the harmful effects of water vapour.
Conclusion
Understanding the essential parts of an air compressor and how they work together is crucial for any business owner looking to make informed decisions about their equipment. From the heart of the system—the compressor motor and pump—to the supporting components like air receivers, filters, and valves, each part plays a vital role in ensuring your system operates efficiently and reliably.
By following best practices in maintenance and setup, such as ensuring proper ventilation, controlling humidity, and preventing oil contamination, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your compressor and optimize its performance. Avoiding common mistakes, like neglecting air leaks or over-pressurizing the system, will also help you avoid unnecessary costs and keep your operations running smoothly.
A well-maintained air compressor is essential for any industrial operation. Whether you need a new system, regular maintenance, or a rental solution, Air to Air Engineering has you covered. We specialize in ELGi and KOBELCO compressors, offering the expertise and support you need to keep your business running efficiently. Reach out to us today to learn more about how we can assist you.
Comprehensive Solutions by Air to Air Engineering
At Air to Air Engineering, we offer a wide range of high-quality air compressors tailored to meet the diverse needs of various industries. Our products are designed with precision engineering and advanced technology to ensure optimal performance, efficiency, and reliability.
Get in touch with us
At Air to Air Engineering, we are committed to providing exceptional customer service and support. Whether you need help selecting the right compressor or require maintenance services, our team is here to assist you. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you choose the right air compressor for your application!



